Lymphoid malignancies involve the clonal proliferation of one or more B or T cells. Every B and T cell expresses distinct receptors on its surface, which give rise to a vastly diverse immune repertoire. Using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, these unique receptor sequences can be used to assess clonality, detect rare clones, and measure somatic hypermutation (SHM).
NGS offers significant advantages over traditional approaches by providing sequence information, giving a more detailed view into repertoire (sub-clonal and intra-clonal) diversity, offering ultra-high sensitivity, and providing greater flexibility to multiplex.

Dr. John DeCoteau MD, FRCPC
Professor Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
Advanced Diagnostic Research Laboratory
University of Saskatchewan

Timothy Looney, PhD
Senior Director of Immuno-Oncology
Quest Diagnostics
On-Demand Webinar
In this on-demand webinar, Timothy Looney describes the advantages of BCR-seq as a tool for determining the somatic hypermutation status of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and highlights emerging translational research applications of BCR-seq as a biomarker discovery tool for adenosine pathway inhibition immunotherapy.
NGS provides sequence-level resolution for clonality assessment, allowing you to detect expanded clones from poly-clonal samples with very high specificity. Integrated bioinformatic tools let you easily assess clonal lineage to better understand the relationship between two clones.
NGS offers a greater level of sensitivity when compared to traditional methods like flow cytometry. The ultralow limit of detection (LoD) of 10-6 (1 in 1,000,000 cells) enables you to detect extremely rare clones that traditional less-sensitive methods can miss.
Using proprietary Ion AmpliSeq™ technology, Oncomine™ immune repertoire assays can target multiple immune receptors in a single reaction, which can lead to increased positive clonality detection rates (>90%) and reduce the need for
secondary testing.
This powerful and sensitive NGS assay can accurately assess clonality and detect rare clones in a range of sample types including blood, bone marrow, and FFPE preserved tissues. Simultaneously sequence multiple receptor targets in a single reaction, including IGH, IgK, IgL rearrangements, as well as kappa deletion element (KDE) containing rearrangements.
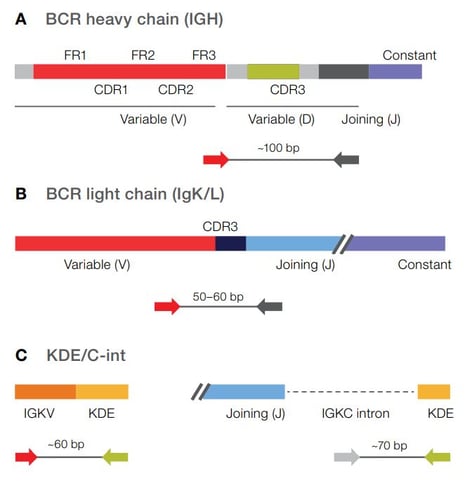
Assess clonality by targeting the CDR3 region of the IGH receptor. Have the flexibility to process DNA or RNA samples. Use RNA input to detect rare B cell clones with high sensitivity (LOD: 10-6), while maximizing cost efficiency.
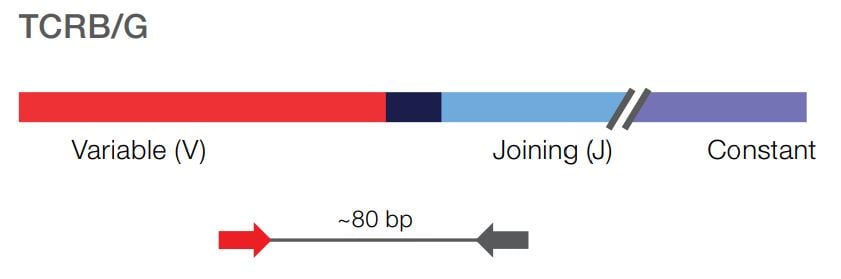
The Oncomine TCR Pan-Clonality Assay specifically interrogates the CDR3 region of the T-cell receptor (TCR) beta and gamma chains. Detect low frequency T-cell clones in peripheral blood, with sensitivity down to 10-6.
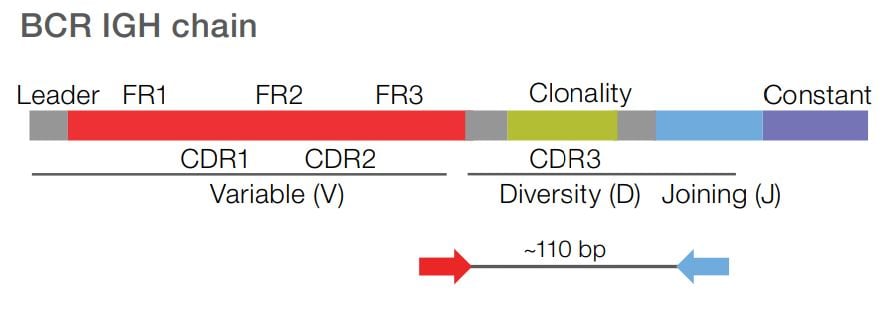
Following V(D)J recombination in developing lymphocytes, the IGHV gene undergoes somatic hypermutation. During this process, a series of point mutations are introduced to help confer greater repertoire diversity and enable higher affinity for
potential antigens.
The degree of somatic hypermutation is a key biomarker relevant for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) research. Long-amplicon NGS assays provide highly accurate IGHV SHM quantification, while enabling efficient batch sample processing and simplifying the workflow when compared to traditional Sanger Sequencing methods.
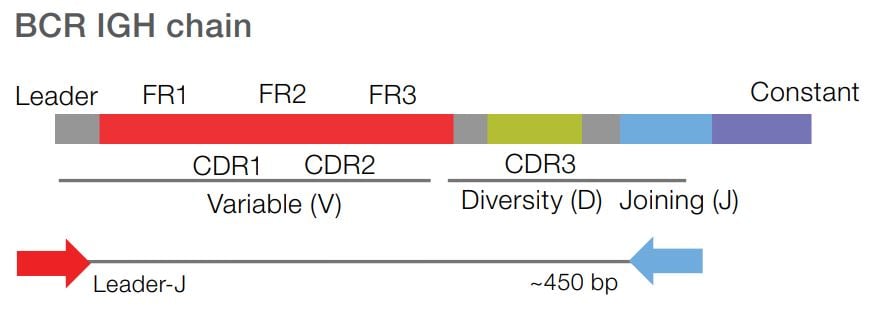
Sequence from the Leader region of the BCR IGHV gene to assess SHM frequency. The Leader-J assay adheres to recommendations by the European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC). These standards in CLL research aid in understanding of the biological and clinical relevance for immunogenetic analysis.
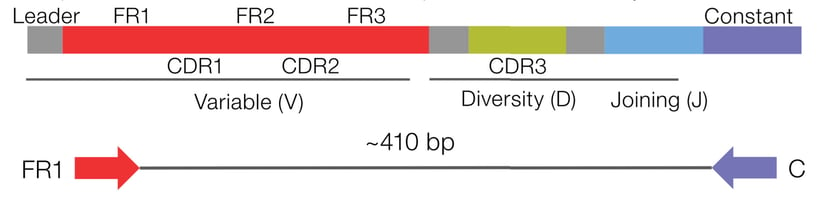
Accurately measure the level of SHM from the FR1 to the constant region of the BCR IGHV gene. Identify all isotypes (and subtypes) to expand immune repertoire research possibilities. Process various sample types, including blood and bone marrow, using a low RNA input requirement (25ng).
Interactive spectratyping plots make it easy to identify clonal expansion within the broader context of the repertoire. Automated reporting features provide detailed information on each clone, including the CDR3 sequence, SHM frequency, clone frequency, and more.
View our posters from the 2022 American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) Meeting
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
We've detected your location to be Japan.
Sorry, you cannot access this website. The content on www.oncomine.com is only intended for healthcare professionals. Formore information on our research solutions, please visit ThermoFisher.com
このウェブサイトは、日本国内の医療関係者の方への情報提供を目的としており、一般の方に対する情報提供を目的としたものではないことをご了承ください。研究用製品の情報はThermoFisher.comよりご覧ください。